When the People’s Republic of China was founded in 1949, the nation’s scientific and technological foundation was strikingly modest. With just over 30 specialized research institutions and fewer than 500 scientists, China’s ambitions seemed far from the powerhouse it is today. Fast forward to 2024, and the nation stands as a global leader in innovation, technological breakthroughs, and research excellence, making the world take notice.
China’s transformation has been monumental.
CGTN
In this report we would be looking at China’s scientific development since its founding up to now.
From Humble Beginnings to Research Giants
China’s transformation has been monumental. The country now boasts over 6.3 million full-time R&D personnel, supported by a robust network of 207 National Engineering Research Centers and 1,798 National Enterprise Technology Centers. In the 2023 Global Innovation Index, China ranked 12th globally, cementing its place as an innovation hub.
Research and development (R&D) spending in China has seen remarkable growth, surpassing $463 billion USD—a 3.2-fold increase over the past decade. This surge not only signifies the government’s commitment to innovation but also highlights the critical role of private enterprises in driving R&D efforts. The intensity of this investment, representing 2.6% of China’s GDP, showcases the government’s strategic focus on fostering technological advancements and economic growth through scientific research.
China has firmly positioned itself as a leader in the global research community, producing over 57,000 highly cited papers, which make up 30.8% of the global total. This impressive output reflects the nation’s robust scientific infrastructure, a highly skilled workforce, and significant funding in both public and private sectors. The number of highly cited scientists has risen to 1,275 by June 2024, placing China at the forefront of global research and innovation. This concentration of talent and resources is not only beneficial for the nation’s progress but also contributes to international scientific advancements, attracting global researchers and fostering collaboration.
Moreover, the rise in China’s R&D spending is complemented by an increase in the quality and impact of its research. Chinese universities and research institutions have developed a strong reputation for excellence in various fields, including artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and renewable energy. This has been driven by targeted government policies, such as the “Made in China 2025” initiative, which aims to elevate the country’s manufacturing and technological prowess. The initiative emphasizes the importance of innovation-driven development and the integration of advanced technologies into key industries, further boosting China’s R&D capabilities.
Patents and Corporate Innovation
China’s advancements are also mirrored in its patent portfolio. By mid-2024, the country held over 4.4 million valid domestic invention patents, with 72.8% of these owned by enterprises. This underscores a wave of corporate innovation, driving practical applications of science and technology.
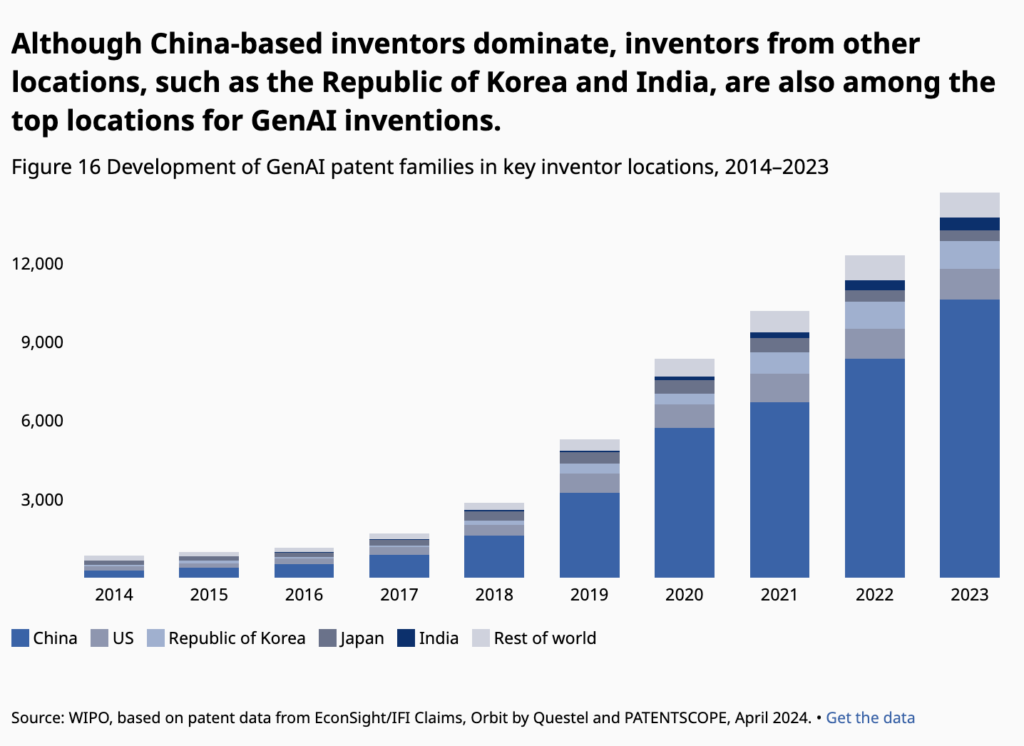
China’s commitment to R&D is also evident in its strategic investments in cutting-edge technologies like AI, quantum computing, and biomedicine. The country’s ability to harness big data, supercomputing, and artificial intelligence has positioned it at the forefront of these transformative technologies, enabling significant advancements in economic efficiency, societal well-being, and global competitiveness. This robust R&D ecosystem not only supports domestic growth but also enhances China’s global influence, fostering closer ties with international research communities and setting the stage for future breakthroughs.
Space Exploration: Reaching for the Stars
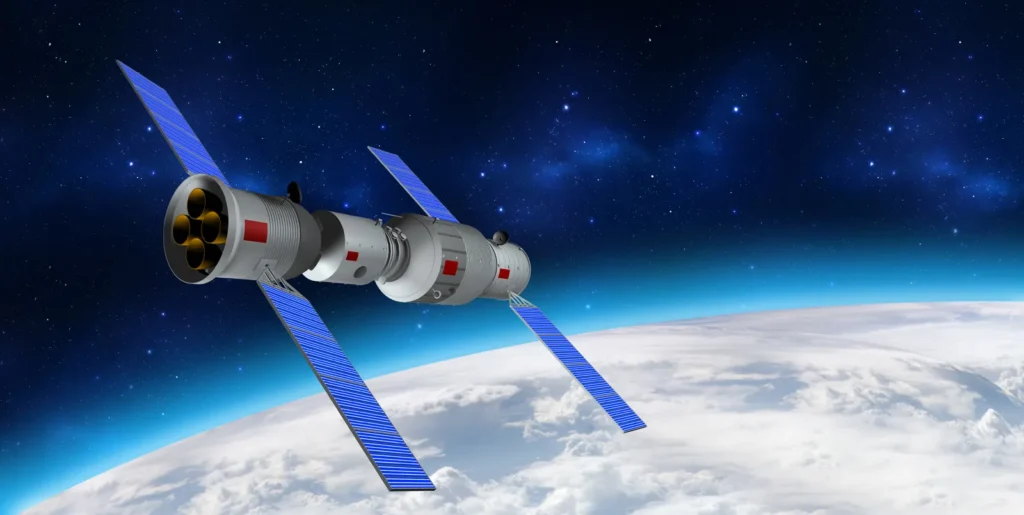
China’s space program exemplifies its technological ambition. From launching its first satellite, Dong Fang Hong 1, over 50 years ago to establishing the Tiangong space station in 2022, the nation has made giant leaps in space exploration. In 2024, the Chang’e 6 mission returned the world’s first samples from the Moon’s far side, while the Zhurong Mars rover showcased China’s prowess in interplanetary exploration.
Exploring Earth’s Frontiers
China’s quest for discovery isn’t limited to space. In 2020, the Fendouzhe deep-sea submersible made history by reaching the bottom of the Mariana Trench, one of the Earth’s deepest points. This achievement marked a significant milestone in China’s ocean exploration efforts, showcasing the country’s determination to explore the unknown depths of our planet.
China’s quest for discovery spans from the Fendouzhe submersible reaching the Mariana Trench to FAST’s groundbreaking pulsar discoveries.
Researcher daily
On land, China has also made remarkable advancements with the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), the world’s largest single-dish radio telescope. Since its launch in 2016, FAST has made groundbreaking discoveries, including over 900 pulsars, significantly enhancing our understanding of the universe. These accomplishments highlight China’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of scientific exploration both on Earth and beyond.
Supercomputing and Telecommunications
In supercomputing, machines like the Sunway TaihuLight and Tianhe-3 have placed China among the global elite. These systems power advancements in artificial intelligence, climate science, and healthcare. Meanwhile, in telecommunications, China leads the world with over 3.7 million 5G base stations as of April 2024, ensuring high-speed connectivity for millions.

However, China’s supercomputer Sunway TaihuLight has fallen to sixth place on the Top500 due to the country’s reluctance to share data with the German ranking agency, prompted by worsening relations with the US. Chinese supercomputing research institutions have ceased submitting data to the ranking due to trade frictions and US sanctions targeting Chinese entities involved in supercomputing.
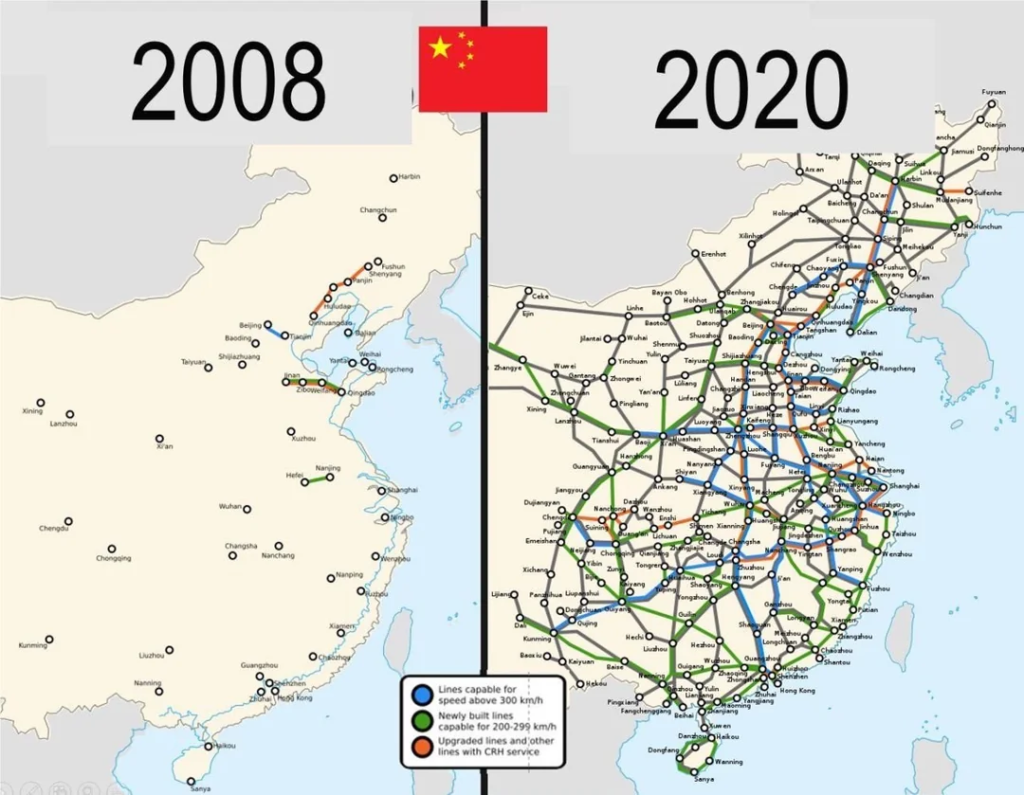
High-Speed Innovation for a High-Tech Future
China’s innovation isn’t confined to research labs—it’s visible in high-speed trains, electric vehicles, drones, AI-powered gadgets, and other cutting-edge products. These advancements symbolize the nation’s commitment to high-quality development driven by science, technology, and innovation.
From its humble beginnings in 1949 to its current status as a technological superpower, China’s journey is a testament to the transformative power of strategic investment, innovation, and ambition. As the nation continues to explore new frontiers, its impact on the global stage is set to grow even further.




